

Sentinel是Redis高可用性的解决方案:由一个或多个Sentinel实例组成的Sentinel系统可以监控多个主服务器,以及这些主服务器下的所有 从服务器,如下图所示:
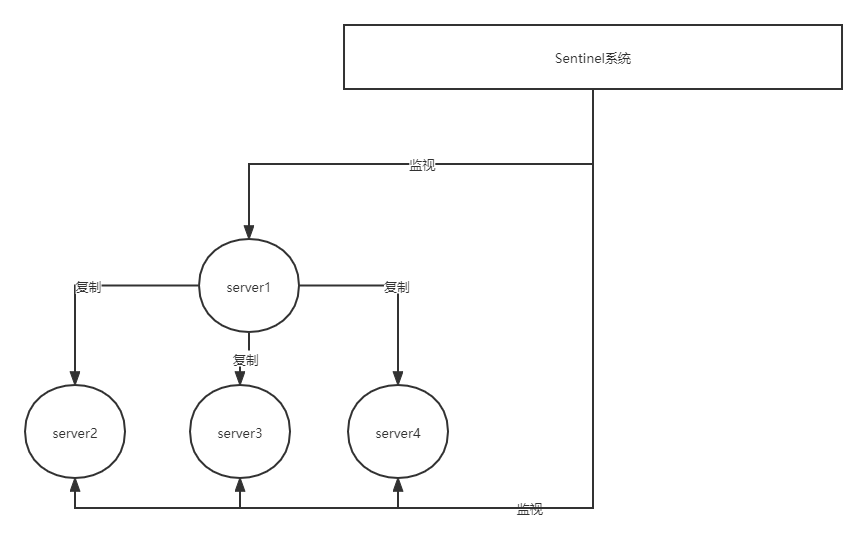
从图中可以看到,当前主服务器server1,三个从服务是server2,server3,server4,而Sentinel系统监视所有四个服务器
假设这时,主服务器server1进入下线状态,那么从服务器server2、server3、server4对主服务器的复制会被终止,并且Sentinel系统会察觉server1已经下线
会执行故障转移操作:
1)、Sentinel系统会挑选server1属下的一个从服务器,并将这个被选中的从服务器升级为新的主服务器
2)、Sentinel系统会向server1下所有的从服务器发送新的复制指令,让他们成为新的主服务器的从服务器,当所有从服务器都开始复制新的主服务器时,故障转移操作执行完毕
3)、另外,Sentinel还会继续监视已下线的server1,并在他重新上线时,将他设置为新的主服务器的从服务器
启动初始化Sentinel
$ redis-sentinel /path/to/your/sentinel.conf
或者命令
$ redis-server /path/to/your/sentinel.conf --sentinel
源码在初始化server的时候可以看到
server.sentinel_mode = checkForSentinelMode(argc,argv);
=====>
int checkForSentinelMode(int argc, char **argv) {
int j;
if (strstr(argv[0],"redis-sentinel") != NULL) return 1;
for (j = 1; j < argc; j++)
if (!strcmp(argv[j],"--sentinel")) return 1;
return 0;
}
具体初始化逻辑在于:
/* We need to init sentinel right now as parsing the configuration file
* in sentinel mode will have the effect of populating the sentinel
* data structures with master nodes to monitor. */
if (server.sentinel_mode) {
initSentinelConfig();
initSentinel();
}
在哨兵模式中,执行的语句有限制
struct redisCommand sentinelcmds[] = {
{"ping",pingCommand,1,"",0,NULL,0,0,0,0,0},
{"sentinel",sentinelCommand,-2,"",0,NULL,0,0,0,0,0},
{"subscribe",subscribeCommand,-2,"",0,NULL,0,0,0,0,0},
{"unsubscribe",unsubscribeCommand,-1,"",0,NULL,0,0,0,0,0},
{"psubscribe",psubscribeCommand,-2,"",0,NULL,0,0,0,0,0},
{"punsubscribe",punsubscribeCommand,-1,"",0,NULL,0,0,0,0,0},
{"publish",sentinelPublishCommand,3,"",0,NULL,0,0,0,0,0},
{"info",sentinelInfoCommand,-1,"",0,NULL,0,0,0,0,0},
{"role",sentinelRoleCommand,1,"l",0,NULL,0,0,0,0,0},
{"client",clientCommand,-2,"rs",0,NULL,0,0,0,0,0},
{"shutdown",shutdownCommand,-1,"",0,NULL,0,0,0,0,0}
};
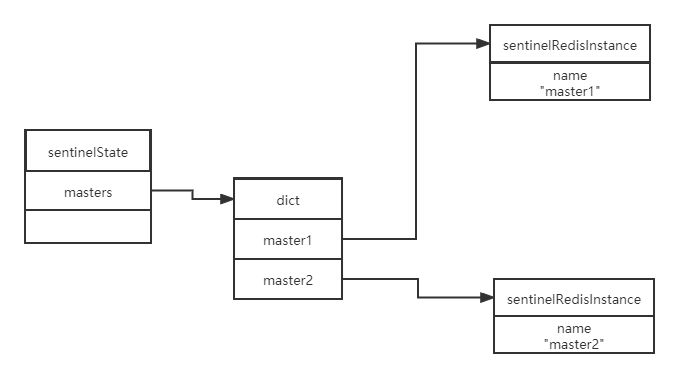
初始化Sentinel时候,需要初始化Sentinel状态
struct sentinelState {
uint64_t current_epoch; /* 当前纪元,用于实现故障转移 */
// 保存了所有被这个sentinel监视的主服务器,key为主服务器的name,value为指向sentinelRedisInstance结构的指针
dict *masters;
}
typedef struct sentinelRedisInstance {
//标识符,实例当前的状态
int flags;
//实例的名称
char* name;
//实例的地址
sentinelAddr* addr;
...
}
如下如所示,结构:
初始化sentinel的最后一步就是创建连向监视主服务器的网络连接,sentinel将成为主服务器的客户端,它可以向主服务器发送命令,该部分在serverCron中
/* Run the Sentinel timer if we are in sentinel mode. */
run_with_period(100) {
if (server.sentinel_mode) sentinelTimer();
}
===>
void sentinelTimer(void) {
sentinelCheckTiltCondition();
sentinelHandleDictOfRedisInstances(sentinel.masters);
sentinelRunPendingScripts();
sentinelCollectTerminatedScripts();
sentinelKillTimedoutScripts();
/* We continuously change the frequency of the Redis "timer interrupt"
* in order to desynchronize every Sentinel from every other.
* This non-determinism avoids that Sentinels started at the same time
* exactly continue to stay synchronized asking to be voted at the
* same time again and again (resulting in nobody likely winning the
* election because of split brain voting). */
server.hz = REDIS_DEFAULT_HZ + rand() % REDIS_DEFAULT_HZ;
}
===>
sentinelHandleDictOfRedisInstances(ri);
===>
sentinelReconnectInstance(ri);
===>
ri->cc = redisAsyncConnectBind(ri->addr->ip,ri->addr->port,REDIS_BIND_ADDR);
连接成功之后发送"ping"
/* Send a PING ASAP when reconnecting. */
sentinelSendPing(ri);
说到Redis的同步异步流程,需要了解redis的Hiredis模块,它涵盖了所有的同步异步操作
所谓的同步操作,就是以阻塞的方式向Redis服务器建链,发送命令,接收命令回复。使用同步操作API,主要涉及以下三个API函数:
//创建连接
redisContext *redisConnect(const char *ip, int port);
//发送redis命令
void *redisCommand(redisContext *c, const char *format, ...);
//接收返回的数据
void freeReplyObject(void *reply);
异步操作流程:
redisContext *redisConnectBindNonBlock(const char *ip, int port, const char *source_addr);
在sentinelReconnectInstance中可以看到后续的事件绑定操作
redisAeAttach(server.el,ri->cc);
==>
redisContext *c = &(ac->c);
redisAeEvents *e;
/* Nothing should be attached when something is already attached */
if (ac->ev.data != NULL)
return REDIS_ERR;
/* Create container for context and r/w events */
e = (redisAeEvents*)zmalloc(sizeof(*e));
e->context = ac;
e->loop = loop;
e->fd = c->fd;
e->reading = e->writing = 0;
/* Register functions to start/stop listening for events */
ac->ev.addRead = redisAeAddRead;
ac->ev.delRead = redisAeDelRead;
ac->ev.addWrite = redisAeAddWrite;
ac->ev.delWrite = redisAeDelWrite;
ac->ev.cleanup = redisAeCleanup;
ac->ev.data = e;
===>
redisAeAddRead方法中创建了文件事件,从而和之前的epoll挂上钩了
其实除了上面建立通信的连接之外,还有一个订阅连接,这个链接专门用于订阅主服务器的__sentinel__:hello频道
#define SENTINEL_HELLO_CHANNEL "__sentinel__:hello"
//绑定流程和之前一样
ri->pc = redisAsyncConnectBind(ri->addr->ip,ri->addr->port,REDIS_BIND_ADDR);
retval = redisAsyncCommand(ri->pc,
sentinelReceiveHelloMessages, NULL, "SUBSCRIBE %s",
SENTINEL_HELLO_CHANNEL);
if (retval != REDIS_OK) {
/* If we can't subscribe, the Pub/Sub connection is useless
* and we can simply disconnect it and try again. */
sentinelKillLink(ri,ri->pc);
return;
}
当2个连接都创建成功后,需要去获取服务器相关的信息了
sentinelHandleRedisInstance.c/sentinelSendPeriodicCommands
/* Send INFO to masters and slaves, not sentinels. */
retval = redisAsyncCommand(ri->cc,
sentinelInfoReplyCallback, NULL, "INFO");
if (retval == REDIS_OK) ri->pending_commands++;
//回调方法sentinelInfoReplyCallback中会处理redis server返回的数据信息并且处理
//一方面是服务器的信息,如果run_id,记录的是服务器的运行id
//另一方面,从服务器信息,从服务器都是以"slave" 字符串开头记录行记录
频道信息发送
else if ((now - ri->last_pong_time) > ping_period) {
/* Send PING to all the three kinds of instances. */
sentinelSendPing(ri);
} else if ((now - ri->last_pub_time) > SENTINEL_PUBLISH_PERIOD) {
/* PUBLISH hello messages to all the three kinds of instances. */
sentinelSendHello(ri);
}
频道信息的主体是payload,包括了当前sentinel的信息
接下来的部分
//检测每个实例下是否出现了断开的情况
sentinelCheckSubjectivelyDown(ri);
/* Check if we are in need for a reconnection of one of the
* links, because we are detecting low activity.
*
* 1) Check if the command link seems connected, was connected not less
* than SENTINEL_MIN_LINK_RECONNECT_PERIOD, but still we have a
* pending ping for more than half the timeout. */
if (ri->cc &&
(mstime() - ri->cc_conn_time) > SENTINEL_MIN_LINK_RECONNECT_PERIOD &&
ri->last_ping_time != 0 && /* Ther is a pending ping... */
/* The pending ping is delayed, and we did not received
* error replies as well. */
(mstime() - ri->last_ping_time) > (ri->down_after_period/2) &&
(mstime() - ri->last_pong_time) > (ri->down_after_period/2))
{
sentinelKillLink(ri,ri->cc);
}
/* 2) Check if the pubsub link seems connected, was connected not less
* than SENTINEL_MIN_LINK_RECONNECT_PERIOD, but still we have no
* activity in the Pub/Sub channel for more than
* SENTINEL_PUBLISH_PERIOD * 3.
*/
if (ri->pc &&
(mstime() - ri->pc_conn_time) > SENTINEL_MIN_LINK_RECONNECT_PERIOD &&
(mstime() - ri->pc_last_activity) > (SENTINEL_PUBLISH_PERIOD*3))
{
sentinelKillLink(ri,ri->pc);
}
对于不断重连在于外层轮询中去创建连接,轮询中已经包含了slaves,sentinels模块等:
void sentinelHandleDictOfRedisInstances(dict *instances) {
dictIterator *di;
dictEntry *de;
sentinelRedisInstance *switch_to_promoted = NULL;
/* There are a number of things we need to perform against every master. */
di = dictGetIterator(instances);
while((de = dictNext(di)) != NULL) {
sentinelRedisInstance *ri = dictGetVal(de);
sentinelHandleRedisInstance(ri);
if (ri->flags & SRI_MASTER) {
sentinelHandleDictOfRedisInstances(ri->slaves);
sentinelHandleDictOfRedisInstances(ri->sentinels);
if (ri->failover_state == SENTINEL_FAILOVER_STATE_UPDATE_CONFIG) {
switch_to_promoted = ri;
}
}
}
if (switch_to_promoted)
sentinelFailoverSwitchToPromotedSlave(switch_to_promoted);
dictReleaseIterator(di);
}
故障转移的源码逻辑
1)、从已下线的主服务器属下的所有从服务器里面,挑选一个从服务器,并转换为主服务器
case SENTINEL_FAILOVER_STATE_SELECT_SLAVE:
sentinelFailoverSelectSlave(ri);
break;
//此处从 从服务器中选择一个节点作为主服务器
void sentinelFailoverSelectSlave(sentinelRedisInstance *ri) {
sentinelRedisInstance *slave = sentinelSelectSlave(ri);
/* We don't handle the timeout in this state as the function aborts
* the failover or go forward in the next state. */
if (slave == NULL) {
sentinelEvent(REDIS_WARNING,"-failover-abort-no-good-slave",ri,"%@");
sentinelAbortFailover(ri);
} else {
sentinelEvent(REDIS_WARNING,"+selected-slave",slave,"%@");
slave->flags |= SRI_PROMOTED;
ri->promoted_slave = slave;
ri->failover_state = SENTINEL_FAILOVER_STATE_SEND_SLAVEOF_NOONE;
ri->failover_state_change_time = mstime();
sentinelEvent(REDIS_NOTICE,"+failover-state-send-slaveof-noone",
slave, "%@");
}
}
2)、让已下线主服务器下的所有从服务器改为复制新的主服务器
sentinel.c/sentinelFailoverReconfNextSlave
/* Send SLAVEOF <new master>. */
retval = sentinelSendSlaveOf(slave,
master->promoted_slave->addr->ip,
master->promoted_slave->addr->port);
3)、已下线的主服务器设置为新的主服务器的从服务器