

Redis服务器将所有数据库都保存在服务器状态redis.h/redisServer结构的db数组中, db数组的每个项都是一个redis.h/redisDb结构,每个redisDb结构代表一个数据库:
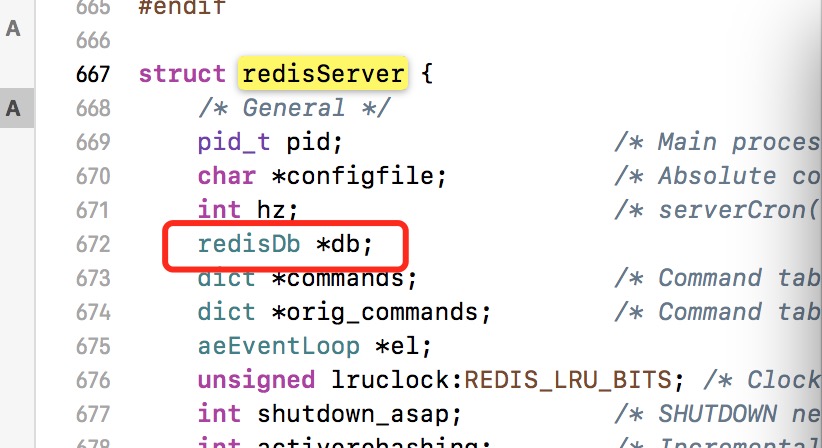
在初始化服务器时,程序会根据服务器状态的dbnum属性来确定创建多少个数据库:
struct redisServer {
....
int dbnum; /* Total number of configured DBs */
....
}
dbnum属性的值有服务器配置的database决定 ,默认情况下,为16,所以Redis默认会创建16个数据库
typedef struct redisDb {
dict *dict; /* The keyspace for this DB */
dict *expires; /* Timeout of keys with a timeout set */
dict *blocking_keys; /* Keys with clients waiting for data (BLPOP) */
dict *ready_keys; /* Blocked keys that received a PUSH */
dict *watched_keys; /* WATCHED keys for MULTI/EXEC CAS */
struct evictionPoolEntry *eviction_pool; /* Eviction pool of keys */
int id; /* Database ID */
long long avg_ttl; /* Average TTL, just for stats */
} redisDb;
结构如下:
-----
|redis|
-----
|.....|
-----
| db | -> db[0] | db[1] | ... | db[15]
-----
在服务器内部,客户端状态redisClient结构的db属性记录了客户端当前的目标数据库,这个属性是指向redisDb结构的指针
struct redisClient {
//记录客户端当前正在使用的数据库
redisDb *db;
}
这也正是select 切换数据库的原理
数据库键空间,在上面redisDb结构中dict字典保存了数据库中的所有键值对
举个例子:
set message "hello world"
那么在数据结构中表示为:
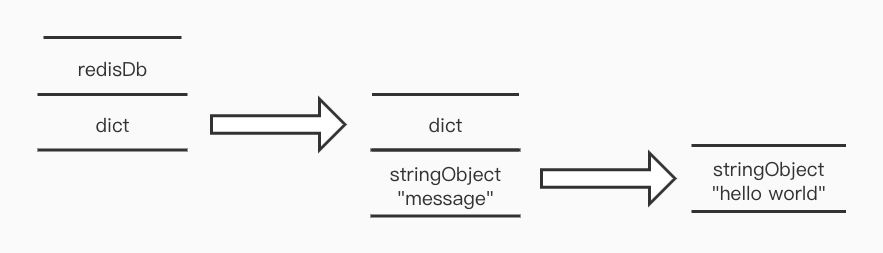
添加新的键值对到数据库,实际上也就是将键值对添加到dict指针里面去
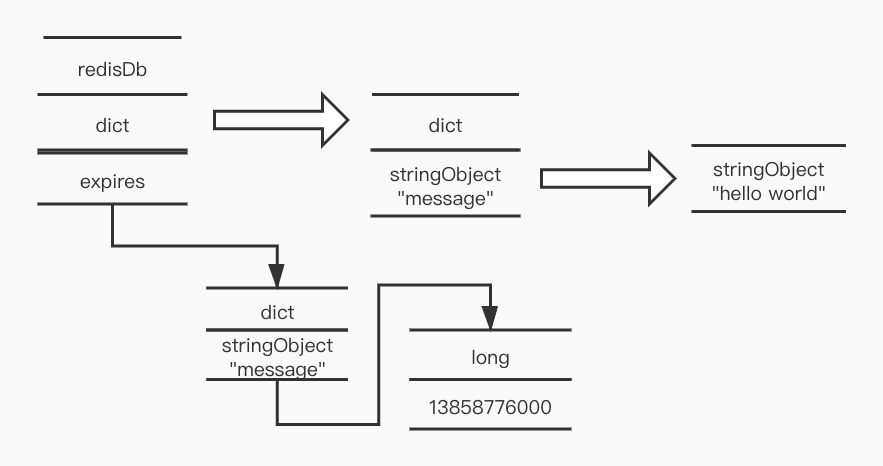
对于键的生存时间或过期时间
通过expire或者pexpire命令,客户端可以以秒或者毫秒精度为数据中的某个键设置生存时间
set key value
expire key 5
// 表示5秒之后失效
// redisDb中正好保存了过期时间,字段为expires
结构图如下:
Redis主体上有3种过期键删除策略
定时删除
定时删除对于内存是友好的,通过定时器,定时删除策略可以保证过期键会尽可能被删除,并释放过期键所占用的内存。 另一方面,定时删除策略的缺点是,它对cpu是不友好的,需要创建大量的定时器,在现阶段来说并不现实。
惰性删除
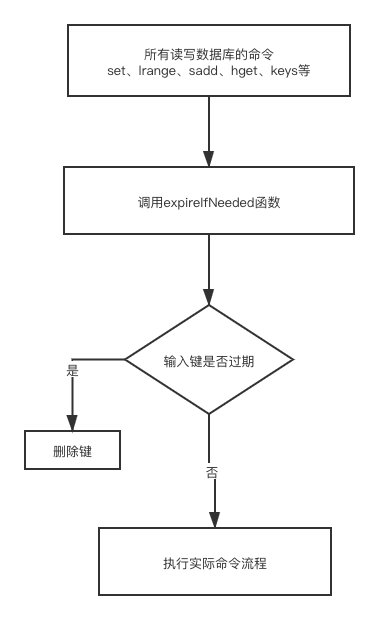
惰性删除对于CPU时间是友好的,程序只有在取出key的时候才进行过期检查,反之对于内存是不友好的。
过期键的惰性删除策略在db.c/expireIfNeeded函数实现,所有读写数据库的Redis命令在执行之前都会调用expireIfNeeded 函数对输入键进行检查。
定期删除
定期删除是2种情况的折中和整合
过期键的定期删除策略由redis.c/activeExpireCycle函数实现的,每当Redis的服务器周期性操作redis.c/serverCron函数 执行时,activeExpireCycle函数就会被调用,分多次遍历服务器中的每个数据库,从数据库的expired字段中随机检查一部分key 的过期时间,并删除其中的过期key。
void databasesCron(void) {
/* Expire keys by random sampling. Not required for slaves
* as master will synthesize DELs for us. */
if (server.active_expire_enabled && server.masterhost == NULL)
activeExpireCycle(ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_SLOW);
}
-------------activeExpireCycle---------------
/* Continue to expire if at the end of the cycle more than 25%
* of the keys were expired. */
do {
unsigned long num, slots;
long long now, ttl_sum;
int ttl_samples;
/* If there is nothing to expire try next DB ASAP. */
if ((num = dictSize(db->expires)) == 0) {
db->avg_ttl = 0;
break;
}
slots = dictSlots(db->expires);
now = mstime();
/* When there are less than 1% filled slots getting random
* keys is expensive, so stop here waiting for better times...
* The dictionary will be resized asap. */
if (num && slots > DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE &&
(num*100/slots < 1)) break;
/* The main collection cycle. Sample random keys among keys
* with an expire set, checking for expired ones. */
expired = 0;
ttl_sum = 0;
ttl_samples = 0;
if (num > ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_LOOKUPS_PER_LOOP)
num = ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_LOOKUPS_PER_LOOP;
while (num--) {
dictEntry *de;
long long ttl;
if ((de = dictGetRandomKey(db->expires)) == NULL) break;
ttl = dictGetSignedIntegerVal(de)-now;
if (activeExpireCycleTryExpire(db,de,now)) expired++;
if (ttl < 0) ttl = 0;
ttl_sum += ttl;
ttl_samples++;
}
/* Update the average TTL stats for this database. */
if (ttl_samples) {
long long avg_ttl = ttl_sum/ttl_samples;
if (db->avg_ttl == 0) db->avg_ttl = avg_ttl;
/* Smooth the value averaging with the previous one. */
db->avg_ttl = (db->avg_ttl+avg_ttl)/2;
}
/* We can't block forever here even if there are many keys to
* expire. So after a given amount of milliseconds return to the
* caller waiting for the other active expire cycle. */
iteration++;
if ((iteration & 0xf) == 0) { /* check once every 16 iterations. */
long long elapsed = ustime()-start;
latencyAddSampleIfNeeded("expire-cycle",elapsed/1000);
if (elapsed > timelimit) timelimit_exit = 1;
}
if (timelimit_exit) return;
/* We don't repeat the cycle if there are less than 25% of keys
* found expired in the current DB. */
} while (expired > ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_LOOKUPS_PER_LOOP/4);